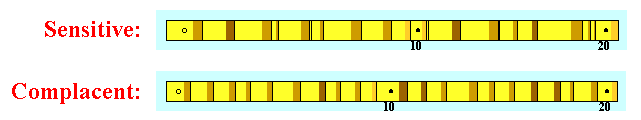
| "Sensitive" tree growth:
- High degree of annual variation
- Example: wide and narrow rings intermixed through time
- Typical of many pine species growing in semi-arid environments
- Limiting growth factor (e.g., rainfall) is highly variable year to year
- Especially true for harsh (steep, rocky) sites (see figure at left)
- Reasonably sensitive ring growth is good:
- Matching patterns of relatively wide and narrows rings across trees is easier when ample variation exists
|